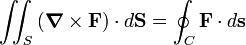Stokes' theorem
In vector analysis and differential geometry, Stokes' theorem is a statement that treats integrations of differential forms.
Vector analysis formulation
In vector analysis Stokes' theorem is commonly written as
where ∇ × F is the curl of a vector field on 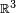 , the vector dS
is a vector normal to the surface element dS, the contour integral is over a closed, non-intersecting path C bounding the open, two-sided surface S. The direction of the vector dS is determined according to the right screw rule by the direction of integration along C.
, the vector dS
is a vector normal to the surface element dS, the contour integral is over a closed, non-intersecting path C bounding the open, two-sided surface S. The direction of the vector dS is determined according to the right screw rule by the direction of integration along C.
Differential geometry formulation
In differential geometry the theorem is extended to integrals of exterior derivatives over oriented, compact, and differentiable manifolds of finite dimension. It can be written as  , where c is a singular cube, and ω is a differential form.
, where c is a singular cube, and ω is a differential form.
| |
Some content on this page may previously have appeared on Citizendium. |