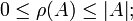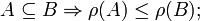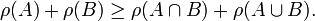Matroid
In mathematics, a matroid or independence space is a structure that generalises the concept of linear and algebraic independence.
An independence structure on a ground set E is a family  of subsets of E, called independent sets, with the properties
of subsets of E, called independent sets, with the properties
-
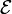 is a downset, that is,
is a downset, that is, 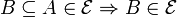 ;
;
- The exchange property: if
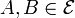 with | B | = | A | + 1 then there exists
with | B | = | A | + 1 then there exists 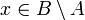 such that
such that 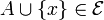 .
.
A basis in an independence structure is a maximal independent set. Any two bases have the same number of elements. A circuit is a minimal dependent set. Independence spaces can be defined in terms of their systems of bases or of their circuits.
Examples
The following sets form independence structures:
-
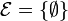 ;
;
-
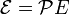 ;
;
- Linearly independent sets in a vector space;
- Algebraically independent sets in a field extension;
- Affinely independent sets in an affine space;
- Forests in a graph.
Rank
We define the rank ρ(A) of a subset A of E to be the maximum cardinality of an independent subset of A. The rank satisfies the following
The last of these is the submodular inequality.
A flat is a subset A of E such that the rank of A is strictly less than the rank of any proper superset of A.
References
- Victor Bryant; Hazel Perfect (1980). Independence Theory in Combinatorics. Chapman and Hall. ISBN 0-412-22430-5.
- James Oxley (1992). Matroid theory. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-853563-5.
| |
Some content on this page may previously have appeared on Citizendium. |