STATE,1,
If one wants to mix together nstates CASPT2 wavefunctions, a nstates single-state, single-reference CASPT2 calculations must be run.
The first calculation must use
{RS2,MIX=nstates, INIT, options
STATE,1,1;}
and the subsequent ones
{RS2,MIX=nstates, options
STATE,1,![]() ;}
;}
for
![]() . Further options can be given, for instance a level shift.
. Further options can be given, for instance a level shift.
At the end of each calculation, the CASPT2 wavefunction is stored, and at the end of the last CASPT2 calculation the Bloch Hamiltonian and the corresponding overlap matrix are automatically assembled and printed. The Hamiltonian is diagonalized after symmetrization following Brandow IJQC 15, 207 (1979), as well as with simple half-sum (averaging). The MS-CASPT2 energy and mixing coefficients printed in each case.
The variable MSENERGY(i) (with i=1,...nstates) is set to the multi-state energies obtained with half-sum diagonalization. If a Level Shift is present, MSENERGY(i) contains the multi-state energies obtained with half-sum diagonalization of the Bloch Hamiltonian whose diagonal elements (CASPT2 energies) have been corrected with the level shift.
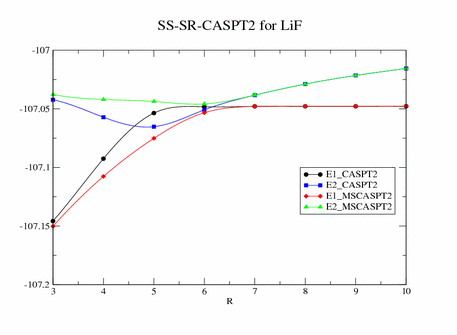
Example: SS-SR-CASPT2 calculation for LiF
Input: lif_sr_mscaspt2.com Output: lif_sr_mscaspt2.out
This produces the plot
molpro@molpro.net